Blog
Electricity has a crucial role to play in addressing the decarbonization across many industries. Shipping is no exception as well. There’s a growing need for a change in the power supply of vessels such as ferries, tankers, bulk carriers, container ships, cruisers, and many others. Along with environmental concerns and regulatory compliances around the world, there are clear economic benefits from the technology that hat allows ships to plug into the local electrical grid while docked at port. This alternative technology that we are talking about is the Onshore power supply.
What is Onshore Power Supply OPS?
OPS is a system that enables electrical power for the ships docked at port terminals from the shore-side electrical grid. It significantly reduces pollutants emissions and greenhouse gases while the ship is at berth. Along with the reduction of carbon emissions for both the vessel and port environment, Onshore Power Supply (OPS) also reduces noise, lowers costs, and enhances the working conditions for seafarers aboard the vessel.
A typical OPS installation requires a building that houses the necessary technical equipment, that usually includes switchgear, transformers, and frequency converters. This equipment is used to adapt the shore’s electrical characteristics, such as voltage and frequency, to match those of the ship.
Based on the situational analyses, we can offer a customizable solution for OPS, consisting of ehouses and electrical equipment tailored to meet the demands of the port. There are 5 different types of OPS systems based on the specific port requirements and vessel types. When deciding about the OPS type, certain factors such as power demand, infrastructure investment, and environmental regulations should be considered.
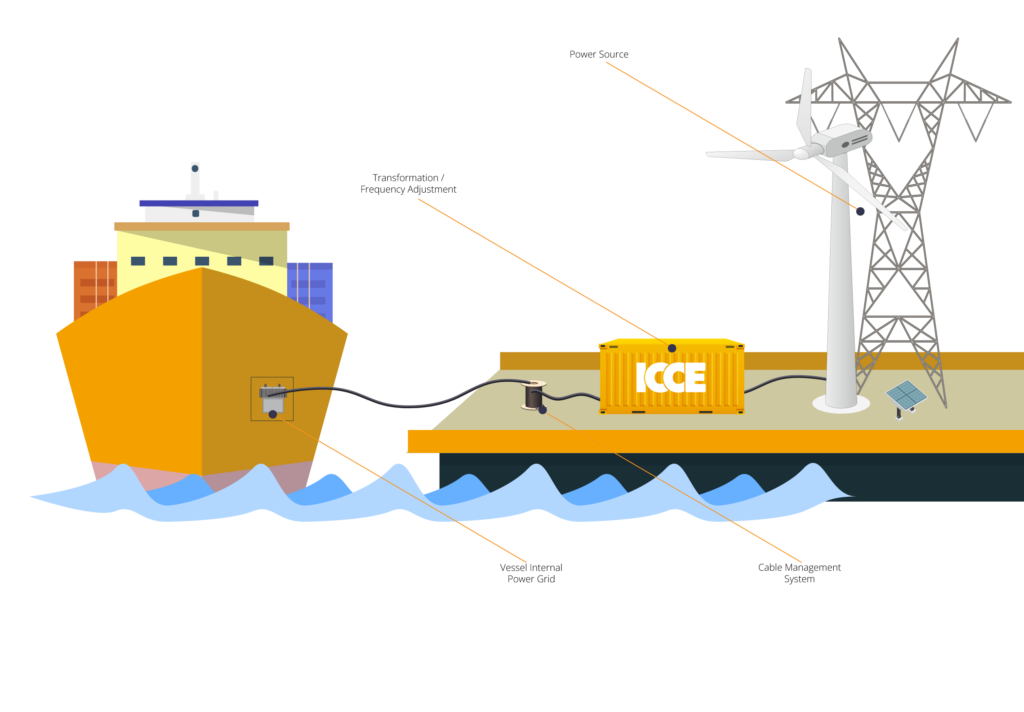
Onshore Power Supply System Types:
High Voltage Shore Connection (HVSC) – HVSC systems supply power to ships at high voltages. They are ideal for HVSC systems to supply power to ships at high voltages. Voltage Levels: 6.6 kV, 11 kV or above.
Low Voltage Shore Connection (LVSC) – LVSC systems supply power to ships at low voltage (400-690 V). These systems are suitable for smaller vessels such as ferries, cruise ships, and smaller cargo ships. Voltage Levels: 400-690V.
Hybrid OPS offers a balance between grid power reliability and renewable energy integration. Applications: Combine power from the local grid, renewable energy sources (such as solar and wind), and energy storage systems (such as batteries). Voltage Levels: Common voltage levels include 400V AC for distribution within the port and 11 kV or higher for connection to the grid.
Direct Current (DC) OPS System supplies ships with direct current (DC) power instead of alternating current (AC). Applications: Used for ships with DC onboard systems or when integrating renewable energy sources that generate DC power. Voltage levels: Common voltage levels include 400V DC for distribution within the port and higher voltages (e.g., 1 kV or more) for connection to the grid or renewable energy sources.
Mobile OPS Systems are portable or temporary systems that can be deployed to provide shore power to ships in locations without permanent OPS infrastructure. Applications: Ideal for use in ports where OPS is not yet installed or during temporary operations. Voltage Levels: Any required voltage level, usually low voltage
- Electrical Design, Engineering, and Planning
- Ehouses
- MV/LV Switchgear
- Transformer Stations
- Frequency Converters
- Cable Management System
- Installation on site
- Commissioning & Start-up
